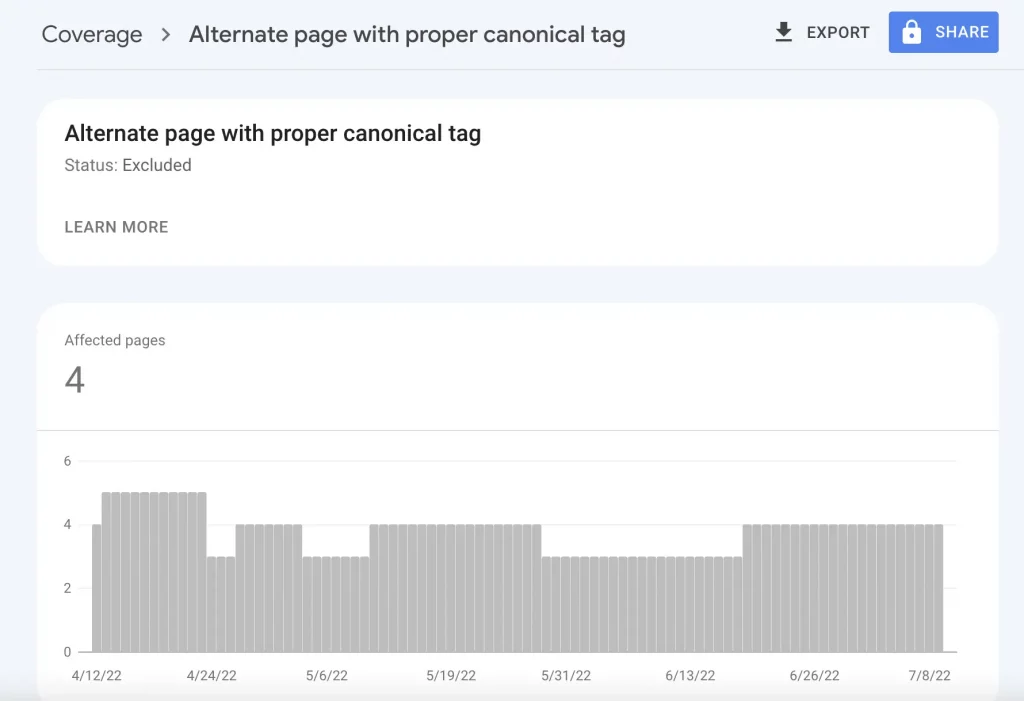
Alternate page with proper canonical tag is one of the coverage issues that is found in the Google search console under the section page –> indexing.
When a web page is affected under this coverage or page indexing condition, it has zero chance of being indexed. So, it is mandatory to check whether the potential or the canonical web page is affected.
In this article, we have detailed how to fix an alternate page with proper canonical tag when a potential web page is affected. Even if a non-potential web page is affected, you’ll learn to save the crawl budget.
What Is Alternate Page With Proper Canonical Tag?
So, what is alternate page with proper canonical? It means Google has found two or more web pages on a website with the same canonical tag.
This can confuse Google in choosing the original page with the proper canonical tag and ends up with Google choosing a web page as original on its own and excluding other web pages.
Is this a huge technical issue? Not until the potential web page gets affected under this coverage issue. It’s mandatory to check and validate to provide the proper canonical tag to the original web pages.
Reasons That Cause Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag Issue
There are multiple reasons that cause this coverage issue. But you should be very clear about whether the potential page is affected. If not, then this issue is just a notification, and it doesn’t require fixation.
The reasons are listed as follows.
1. AMP version of web pages:
AMP is not currently a ranking factor. Yet, a few years back, many website owners believed and optimized their mobile pages with the AMP version.
This is one of the reasons why any of your web pages might be featured on an Alternate page with a proper canonical tag.
For example,
General Version: the7eagles.com/seo-services/
AMP version: the7eagles,com/seo-services/amp/
In this case, these are two URLs that hold the same content. So, Google considers either of these pages as canonical and index them. The other would be excluded from indexing.
Your role here is to check whether the potential URL is indexed or excluded.
2. Protocol like www/non-www http/https:
This is the most common case where we find URLs due to different protocols.
http://example.com/
https://example.com/
http://www.example.com/
https://www.example.com/
Protocols can create multiple URLs with the same content, and only one gets indexed, and others are excluded.
3. Dynamic URLs in Case of Search Parameters
Generally, an e-commerce website or blog website uses a search option to find any product or topic.
It often appears as below:
https://example.com/dresses/cocktail https://example.com/dresses/cocktail?gclid=ABCD
https://example.com/dresses/cocktail?gclid=ABCD&color=red
In the above case, the master or canonical URL will be indexed, and others will be excluded.
4. Pagination:
Pagination is another case that can be excluded under alternate page with proper canonical tag.
This usually occurs when Google bots crawl multiple pages of blogs, author pages, and many more.
The examples are similar to those below
https://example.com/author/page-1 https://example.com/author/page-2
https://example.com/author/page-3
In the above case, the master or canonical URL will be indexed, and others will be excluded.
How to Fix Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag Issue?
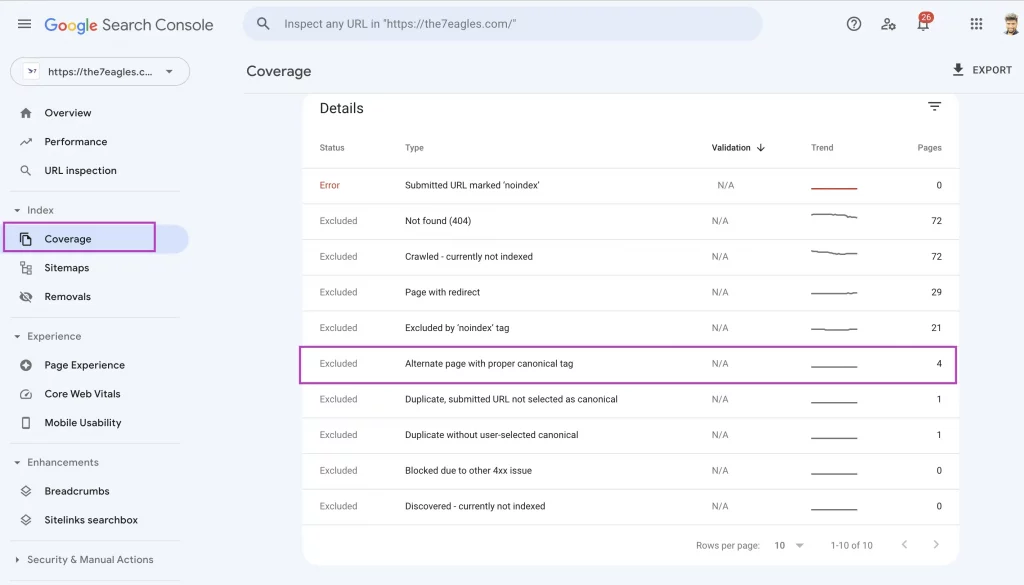
The first step in fixing alternate page with proper canonical tags is to identify the web pages that are affected by this coverage or page indexing issue.
Go to Google search console –> Indexing –> Page. Once in, you will get a dashboard with two options—Not indexed and Indexed.
Under the Not-indexed section, you can get all the affected URLs of alternative page with proper canonical tag
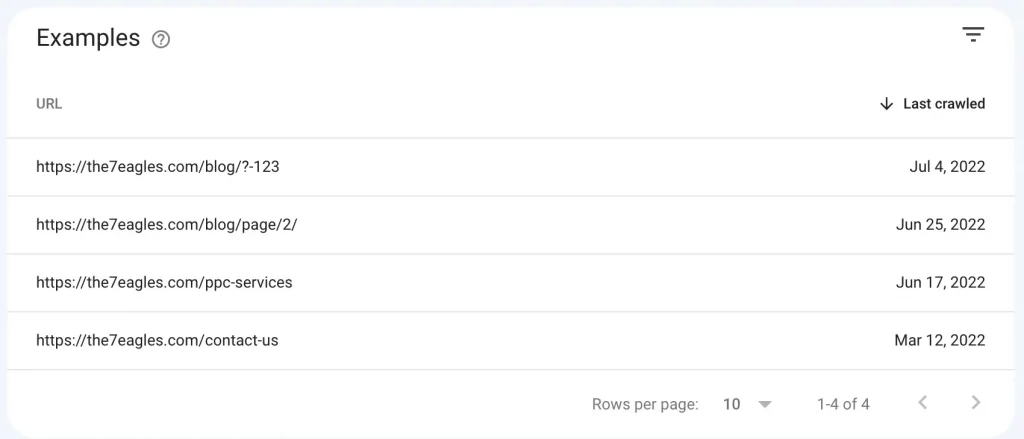
Here are a few ways to fix this issue by following the steps.
1. Use a rel="canonical" Link Tag:
- Use canonical link <link rel=”canonical” href =”https://example.com” /> in the HTML header of the master page.
- Also, insert the duplicate page with the canonical URL of the original page.
- If your canonical page has a mobile version URL, add rel=”alternate” linking to the page.
<link rel="alternate" media="only screen and (max-width: 640px)" href="http://m.example.com/" />
- Add hreflang or redirects (301 & 302) to the appropriate page, if needed.
2. Have the canonical web page in XML Sitemap
Create a sitemap for your website and submit only the canonical URLs that are to be indexed. Try to exclude all the duplicate web pages from the XML sitemap.
If a URL is found in sitemap.xml, all pages are accessible by search engines to be crawled and understand the relevancy. This might end up in Google crawling multiple pages with the same canonical tag.
If you find any duplicate web pages in the XML sitemap, remove them and upload the new sitemap in the Google search console. This will reduce the alternative page with canonical URL issues.
Strictly, sitemaps should not include non-canonical pages.
3. Use 301 redirects to the Original web page
Another solution for fixing alternate page with proper canonical tag is by redirecting the old URLs or protocol issue URLs to the destination page that you need to index.
Suppose the destination web page is reached by multiple URLs as follows:
https://example.com/homehttps://home.example.comhttps://www.example.com
You should use the canonical or the master page with rel=”canonical” and redirect other related pages to them. This makes the original page index.
4. Always Prefer HTTPS over HTTP
Google loves web pages that contain protocols encrypted with SSL certificates (HTTP links).
In the same way, use rel=”canonical” tag of HTTP pages targeting HTTPS pages.
Avoid submitting HTTP pages in Sitemap, and avoid using cracked or unauthorized versions of SSL/TLS certificates.
Finally, implement HSTS. Also, make sure your XML sitemap doesn’t have HTTP web pages.
5. Update content consistently for the Canonical (Original) Web page
One of the best practices to fix this coverage issue is to differentiate the original web page by updating the content consistently.
This will provide a better idea to search engines to understand which is original despite multiple web pages having the same canonical tag.
6. Use Hreflang Tag incase of Multilingual Web pages
Multilingual web pages can also be affected under alternative page with proper canonical tag.
To fix this issue, use the hreflang tag. This tag will provide a clear indication to the search engine on the original web page despite having an identical web page with a different language focus.
7. Internal Linking should be done only to the Original (Canonical) web page
Whenever you do internal linking for relevant anchor text, always use the original web page URL.
Audit all the relevant internal links and validate whether all the links are original URLs. If you find any other identical (duplicate) page URLs, change them.
Internal links are commonly used as the relevancy factor and are one of the ways search engines estimate the original web page.
8. Fix the redirect chain between Web pages of same canonical tag
Redirect chain by any means is harmful to SEO, as it could consume loading speed, crawl budget, and even create coverage issues.
If you find a redirect loop or chain between two or more web pages of the same canonical tag. It’s time to fix this redirect loop, as this loop or chain can confuse search engines to find the actual canonical web page.
Things to Avoid While Fixing Alternative Page with Proper Canonical Tag:
- Never use Robots.txt to block the duplicate page.
- Never use the noindex robots tag.
- Don’t use the Removal of duplicate URLs using the Google Search Console. This might remove the original page from indexing.
- It is not recommended to specify different canonical URLs for the same page using the same or different canonicalization techniques.
How do I fix alternate page with proper canonical tag in WordPress?
1. Identify Duplicate Pages:
- Use Google Search Console’s “Coverage” report to find affected URLs.
- Use a crawling tool like Screaming Frog to scan for duplicate content.
2. Choose the Canonical Version:
- Decide which version of duplicate content you want Google to prioritize.
- Consider factors like relevance, traffic, and backlinks.
3. Set Canonical URLs:
a) Using a WordPress SEO Plugin:
- Install a plugin like Yoast SEO or Rank Math.
- Find the canonical URL setting for each page.
- Enter the canonical URL of the preferred version.
b) Manually Editing Code:
- Access your theme’s header.php file.
- Add the following code within the <head> section:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/canonical-page/”>
Use code with caution. Replace the URL with the actual canonical URL.
4. Use 301 Redirects for Unwanted Pages:
If a page should no longer exist:
Redirect it to the canonical version using a 301 redirect.
Use a plugin like Redirection or manually edit your .htaccess file.
5. Check Internal Links:
- Ensure internal links point to the canonical version.
- Fix any links pointing to non-canonical pages.
6. Monitor and Maintain:
- Regularly check Google Search Console for canonicalization issues.
- Update canonical URLs as needed, especially after content changes.
Looking to Fix Alternate Page with Proper Canonical tag?
Conslusion:
- Alternate page with proper canonical tag is one of the Google Index coverage issues.
- This can harm your potential page if canonical tags are not or are incorrectly mapped.
- You have to check the canonical status (rel link=”canonical”) of the affected page. If it doesn’t target the canonical page, it will be duplicate content.
- Using a sitemap, redirect, and proper canonical tag can fix this issue.
- If you find this process tedious, you can hire us for technical SEO services.