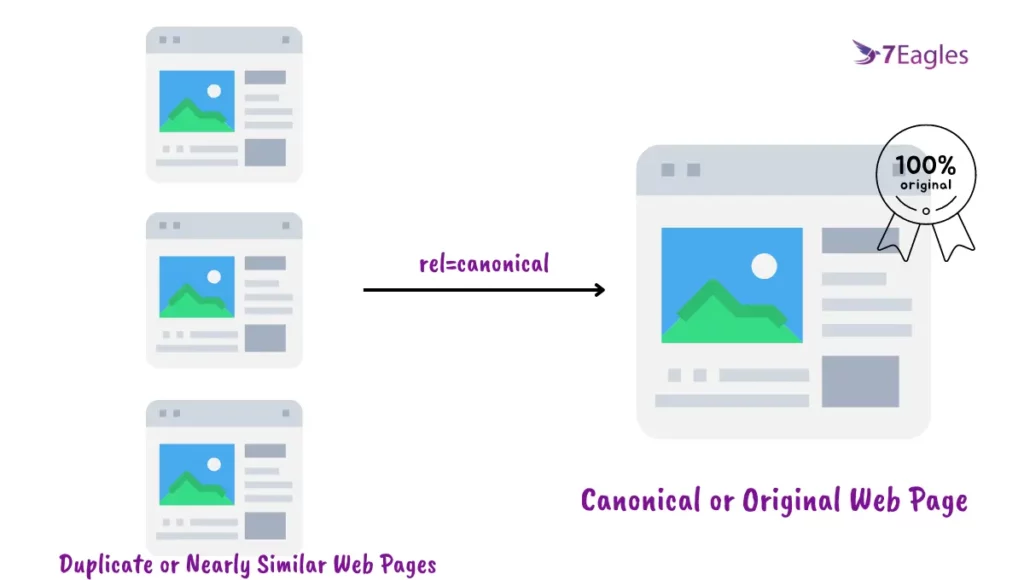
Nowadays, search engines have become too smart to identify duplicate or near duplicate content in a website and exclude it from indexing. They only index the master web page, denoted by a canonical tag( also called rel canonical)
These are never new concepts that need to be given attention; they have been a part of the Google algorithm since 2009.
It’s the role of the website owner or SEO practitioner to provide the canonical URL for the master web page. If failed, the Google choose it’s own web page as canonical as index them.
This could hurt the SEO effort, as it might choose the identical version (duplicate) and not the original web page as canonical. These issues are not common, but still it happens.
What is Canonical Tag?
Canonical Tag is also referred to as canonical URL. It is an HTML code that helps the search engine crawlers to understand the master version of the content.
Many websites have duplicate or near-duplicate content, and this makes it a complicated process for the search engine to find what is original. As search engines only index the original copy of the web page.
Canonical URL helps search engines like Google differentiate both original and duplicate web pages.
Here is the piece of code that informs the canonical version of a web page,
link rel=" canonical" href="https://yourdomain.com/blog/seo-strategy/" />
This an HTML code and should be placed between <head>….</head>
rel=”canonical” -> is the command sent to search engines about the canonical version.
href=”URL” -> Master or Original URL of the web page.
How Does Google Choose Canonical URL of a Web Page?
Indexing is a crucial part of SEO and is the only way that your content can rank in the SERP (search engine result page) to make your website a magnet that attracts organic traffic.
Google’s primary job is to index only the master copy of any content and try to exclude duplicate versions. So, it checks for the original version with the help of user-selected canonical (link rel=”canonical”).
I hope you will go through our article on how a search engine works, in that we have elaborated on the process of indexing. Once the crawling and rendering steps are completed, the search engine looks at its index database to diagnose the original version (canonical) of this web page.
Once it finds that the web page is original, Google starts inspecting user-selected canonical. If both user-selected and Google are in the same line, then the web page will be indexed.
If either the other has a contrast in the canonical URL, Google excludes it as a duplicate, the submitted URL is not selected as canonical from indexing under a page index issue (previously known as coverage issues)
If any page is without user-selected canonical, again there is a chance for the potential web page to be excluded from indexing by duplicate without user-selected canonical.
Why Is Canonical Tag Is Important in SEO?
1. Crawl Budget and Priority
Every search engine crawler allocates a specific amount of crawl budget for every website. Crawlers index the canonical page and exclude duplicate or similar content from indexing.
At the same time, when you provide canonical tags for potential pages, search engines crawl them frequently, and duplicate pages are rarely crawled.
2. Rank Specific Web Page for the Query:
Usually, big websites have various versions of web pages for better user experience on various devices. For example, you can see three various UX/UI for Amazon’s website.
So, there can be many URLs associated with like
https://yourdomain.com/
https://m.yourdomain.com/
https://amp.yourdomain.com/
But, the page to be indexed or ranked should be the original version (https://yourdomain.com/), the canonical tag.
3. To Pass Link Juice to Potential Page:
When a website has duplicate content or relatively similar content, such as dynamic URL or HTTP/HTTPS, the Page rank or link juice can’t be able to pass toward the potential web page.
When the canonical URL is set up for the master and duplicate web pages, the link juice will pass only to the master web page and make it rank in SERP.
4. To Avoid Coverage Issues:
Incorrect implementation of canonical tags causes three Google index coverage issues, They are the following:
All the coverage issues are explained in detail in various blogs, Refer to these blogs if you are interested.
- Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag
- Duplicate, without user-selected canonical
- Duplicate, submitted URL not selected as canonical
So, it is important to optimize your website with proper canonical tag strategies.
Reason for Duplicate Web Pages, If Content Aren't Duplicate:
It does not necessarily need to optimize a web page only when you have duplicate content (copied internal content). Duplicate content or nearly similar issues can arise for the following reasons.
1. URL of Multiple Device Versions:
A website with different designs for all the devices can come under coverage issues, excluding duplicate pages.
- AMP and Non-AMP versions of web pages
- Separate URL for mobile, desktop, and tablet devices
2. Search terms in URL at the end of absolute URL:
Every website has an option to search for any product, service, or blog.
So, when users search for any search term like “protein powder.”
The URL comes as
https://yourdomain.com/?q=protein+powder (URL with search parameter)
https://yourdomain.com (Absolute URL)
So, a URL with the search parameter is a duplicate version of the absolute URL.
3. HTTP and HTTPS version of Web Page:
Another reason is HTTP and HTTPS versions in the crawl queue. This could make the HTTPS version a duplicate version of the user-selected canonical is not implemented.
https://yourdomain.com/
http://yourdomain.com/
4. WWW and Non-WWW Version of Web Pages:
Usually, every website focuses on URL redirect resolution, so the www or non-www version has to redirect to the absolute version of the website.
We suggest keeping URLs with the non-www version.
https://www.yourdomain.com/
https://yourdomain.com/
5. Web Pages with and without Trailing Slashes:
Common issues that we find potential web pages excluded from indexing under alternate pages with proper canonical tags. In most cases, the absolute web page ending with a trailing slash becomes a duplicate.
https://yourdomain.com/seo-strategy/
https://yourdomain.com/seo-strategy
6. Dynamic Web Pages create dynamic URLs:
When a website is dynamic, it creates multiple versions as dynamic URLs in the cases of products (size, color, etc.), and events (session IDs).
https://yourdomain.com/products?category=dresses&color=green
https://yourdomain.com/product/?size=medium
7. Multiple URLs for the same Web Pages:
Sometimes, the blog setting (autosave) might save two URLs (published & edited URLs) before indexing. This also could cause a duplicate issue, and you need the canonical tag to solve this.
https://yourdomain.com/canonical-tag/
https://yourdomain.com/what-is-canonical-tag/
How to Optimize Canonical Tag:
Setting rel=canonical of HTML tag is not the only step to fix canonical issues. Yet, it is the primary step you should be processing while optimizing a web page.
Here are four ways that you should follow to fix the canonical tag issues
- HTTP header
- XML Sitemap
- 301 Redirect
- Internal Links
Canonical tag in HTTP Header:
When you have a PDF or e-book, these web pages are not built-in HTML codes and thus don’t have a header section to set rel=canonical.
In such cases, you can implement the canonical tag in HTTP Header. Also, you can set the canonical tag using the HTTP header for standard web pages too.
Here is a sample of how a canonical tag looks in the HTTP header.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Type: application/pdf Link: <https://yourdomain.com/blog/canonical-tags/>; rel="canonical"
Canonical Web Pages in XML Sitemap:
XML sitemap has a huge role in crawling and indexing web pages. Search engine crawlers believe the URL in sitemap.xml is the master version. So, you should only keep the canonical web pages and exclude non-canonical web pages from sitemap.xml.
Google stated, “We can’t guarantee that all the web pages in the sitemap are canonical, but when it comes to large websites, sitemaps are considered a checkpoint to validate canonical web pages.”
301 Redirect of Duplicate Page to Canonical Page:
301 redirects are one of the fine optimization protocols that have to be performed in when web pages where the duplicate issue arise for the following reasons:
- WWW and non-WWW web pages
- HTTP and HTTPS versions
- URL ending with or without trailing slashes
- Default content in index pages
For example,
https://yourdomain.com/
https://www.yourdomain.com/
http://yourdomain.com/
https://yourdomain.com
https://yourdomain.com/index.php
In the above 5 URLs, the canonical version is https://yourdomain.com/, then you should redirect all other web pages to reach the canonical web page.
Canonical URL Optimization using Internal Links:
Internal links help crawlers to discover new web pages; they help users to navigate informational pages. However, these internal links sometimes can harm the canonical web page from indexing and ranking.
When you place a link over a text, always keep the canonical web page (absolute URL).
When you misplace the canonical URL, i.e., missing slash at the end or www version or HTTP version, etc., can cause an issue in the canonical tag for the absolute URL.
So, always provide the canonical URL while optimizing content with internal links.
Conclusion
Canonical tag in SEO is very crucial for page indexation technique, because when canonical URL is not set, then your master webpage will get affected even though you have good content.
Make sure you have a proper canonical tag on each page, you can also use the WordPress Rankmath plugin to analyze and edit your canonical tag.
Frequently Asked Questions
A canonical tag is an HTML tag that signals search engines which version of a URL is to be considered the primary (canonical) version.
Example :
When you mention this HTML tag,
link rel=” canonical” href=”https://yourdomain.com/” />
We have three domains
“https://yourdomain.com/
https://m.yourdomain.com/
https://amp.yourdomain.com/”
From these three domains, Google considers “https://yourdomain.com/” to be a Canonical URL.
Here are steps to create a canonical tag
Choose which URL you want to use for duplicate content. This chosen URL is called the canonical URL.
Then, link the duplicate pages to the canonical one using a rel=”canonical” link.
Finally, on the canonical page, include a self-referencing canonical tag that points to itself as the canonical page.
Yes, It is good for SEO as Google will index only the main content page with canonical URLs and it helps avoid content duplication.
If you have a page like https://www.domain.com, you can add a rel=”canonical” tag that directs to the same URL, “https://www.domain.com”
Example: <link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.domain.com” />