Have you ever faced Duplicate, Google chose different canonical than user coverage or page indexing issue? Then you might have wondered if it hurts your web page from attracting target traffic.
The answer is yes, sometimes it does. Eventually, it all depends on the web pages that gets excluded under this coverage issue.
In this article, let’s break the ice to learn the concept of this coverage/page indexing issue, how these issues are caused, and how to fix them. Continue reading to learn more.
What is Duplicate, Google Chose Different Canonical Than User?
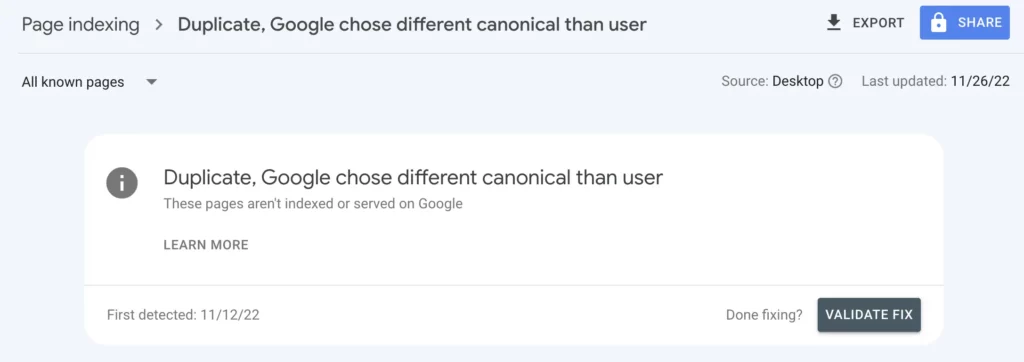
Duplicate, Google chose different canonical than user is a coverage/page indexing issue that happens when Google prefers other version of URL as canonical than the user-declared (website owner) canonical URL.
Google only indexes the canonical version of any web page. Canonical URL is what defines the Google search engine as the original version, and other version of web pages with same content are considered as duplicate.
This coverage issue occurs for the following reasons,
- User declaring canonical URL of duplicate version (misplacing)
- Redirect from original version to duplicate version of web page.
- Providing the same canonical tag as the URL of the duplicate web page.
Duplicate, Google choose different canonical than user is completely different from alternate page with proper canonical tag.
How to find Duplicate, Google Chose Different Canonical Than User?
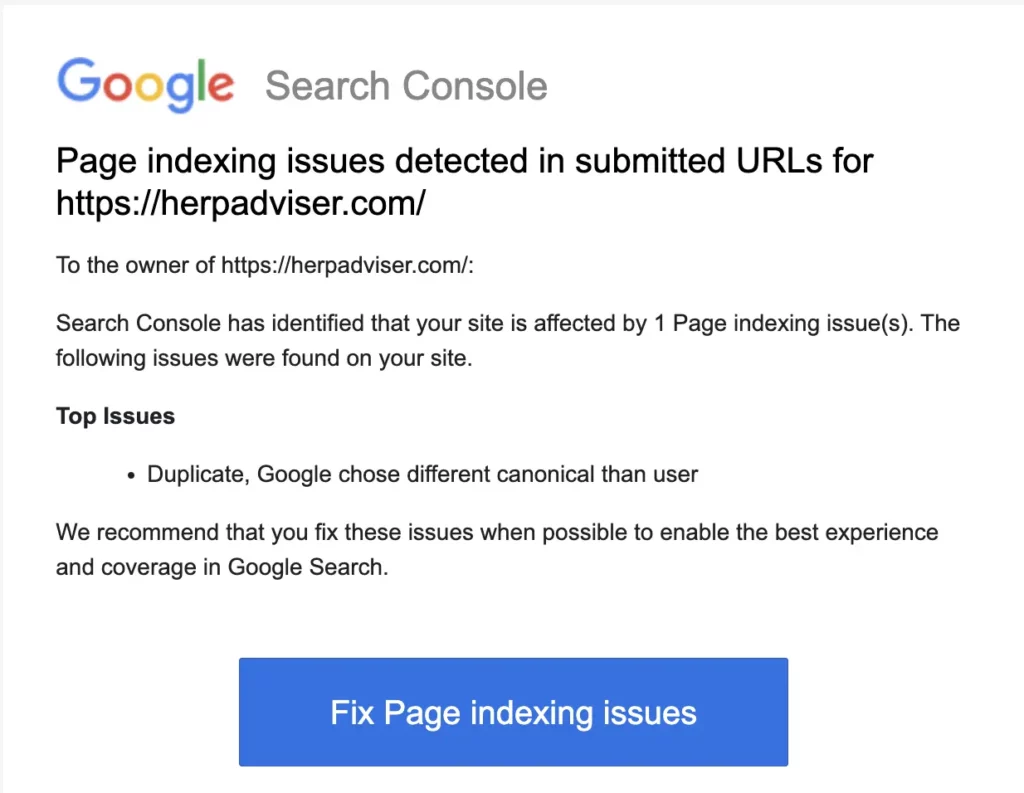
If you have this indexing issue, you will be notified in email that is associated with Google search console. Once you get this mail, login to Google search console.
Then select the property, and move towards Page Section
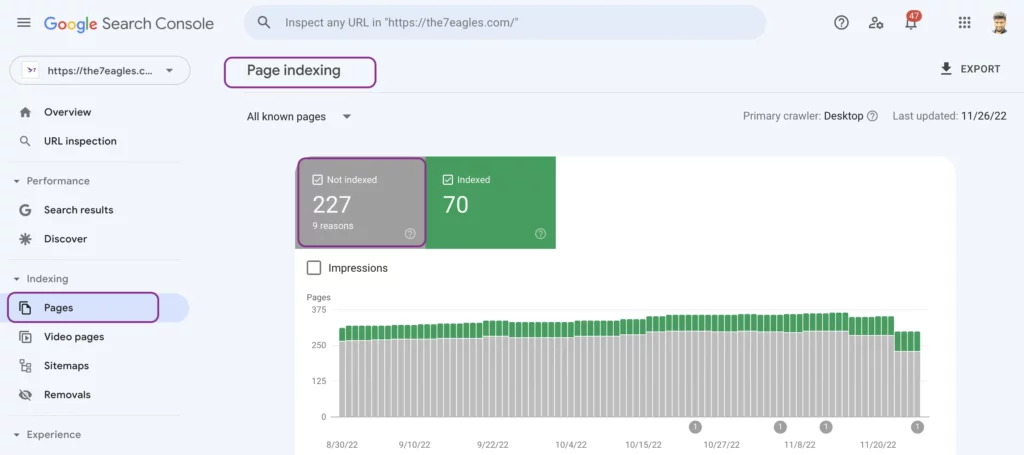
You will get the dashboard which has not indexed, and indexed web pages.
Select the not indexed tab. You will receive all the page indexing issues and the number of URLs affected.
You can select duplicate, Google chose different canonical than user and get the details.
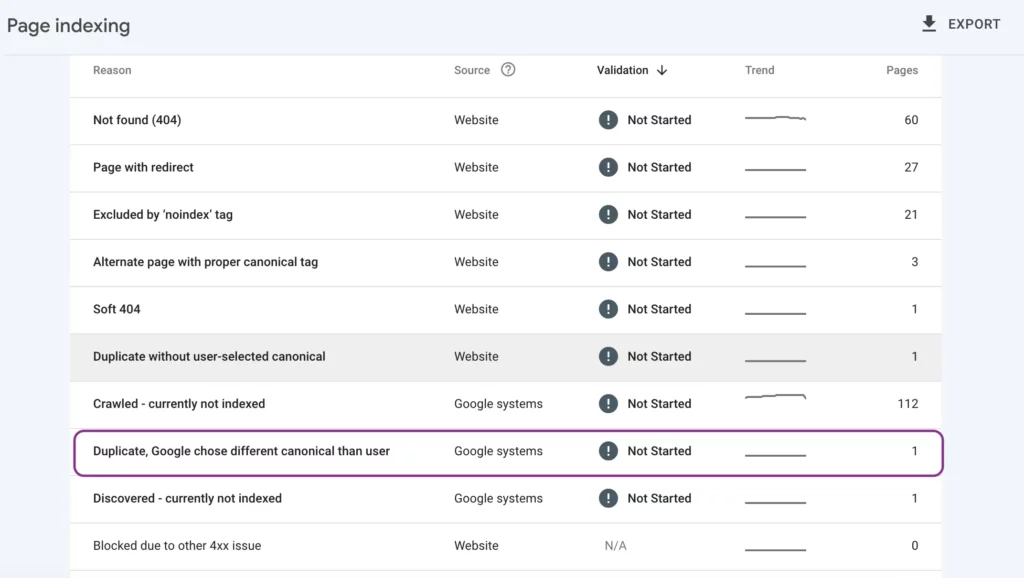
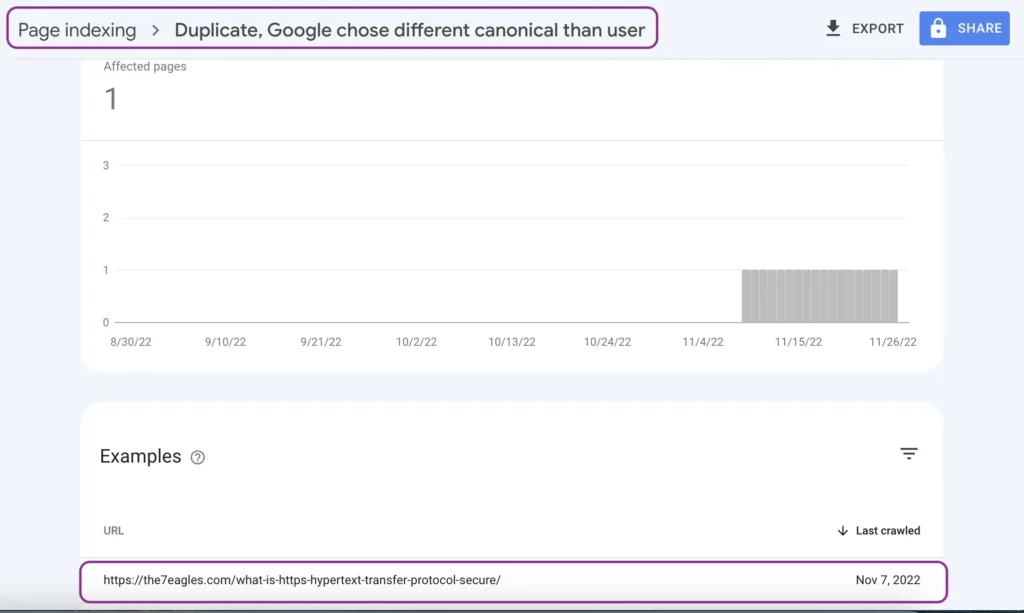
How to fix Duplicate, Google Chose Different Canonical Than User?
It is not tedious to fix this coverage issue. But before that, you need to analyze whether the affected URL is potential to index.
If the excluded URL is not to be indexed, then use 410 HTTP code or use Removal tool in Google search console to remove the URL from Google data base.
Also, check whether the same URL is present in XML sitemap, and remove them.
When the URL excluded is potential to fix, follow these two steps.
1. Validate the Canonical URL of the Web Page:

Here is the above image with HTML codes of a web page, and the highlighted part is the canonical tag of the web page.
<link rel=”canonical” href=” “/>
Scenario 1: If the web page is original, then the canonical URL should be the same as the web page URL.
Scenario 2: When the web page is a duplicate version, the canonical URL should be same as original web page URL.
If you find any mismatch in the above two scenarios, then, change them immediately.
2. Redirect to the Original Web Page:
If the canonical URL of the web page is correct, but Google has identified the duplicate page URL is canonical, please follow the following steps to fix the issue,
- Redirect duplicate web page URL to the original Web page.
- Remove all internal links pointing to the duplicate web page.
- Remove the duplicate web page from the XML sitemap
Once these steps are done, don’t forget to select validate fix in Google Search Console.
Conclusion:
Duplicate, Google chose different canonical than user is a common coverage issue that appears in Google search console. In fact, it doesn’t hurt SEO performance until a potential web page is affected.
If you can’t find ways to fix this issue, don’t panic. You can hire us for holistic technical SEO services.
Google may select a different canonical URL if it believes another page better represents the content or if there are conflicting signals about which URL should be preferred.
Yes, Google can choose to ignore canonical tags, though they generally follow to them as guidelines to consolidate duplicate content.