Are you facing a Page indexing issue – Duplicate submitted URL not selected as canonical in the Google Search Console?
It’s not a big issue, yet, it could cause your potential page to be excluded from indexing when affected by coverage issue. You need to fix immediately, if you find potential web pages are affected.
In this article, let’s break the the complete concept of this coverage/page indexing issue, how these issues are caused, and how to fix them. Stay till the end!
What If Duplicate Submitted URL Not Selected as Canonical?
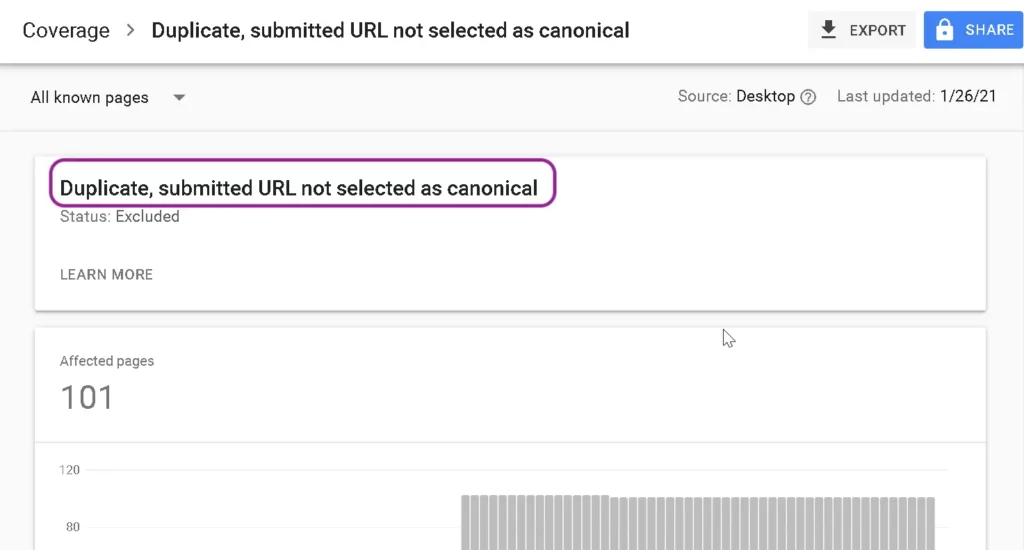
The duplicate, submitted URL not selected as canonical is a common coverage or page indexing issue that appears in the Google search console.
This coverage issue happens when Google finds another web page as canonical (preferred) against the user-selected canonical. Finally, the affected page becomes a duplicate version of the Google-selected canonical.
You should be aware that there are no same URLs of multiple versions like http, or https, www, or non-www. The only difference on this page index issue to duplicate, Google chose different canonical than the user is Google hasn’t finalized the canonical URL.
How to Find Web Pages with Duplicate Submitted URL Not Selected as Canonical?
You can find the issue in the Google Search Console under the section Page once you log in using the associated Gmail.
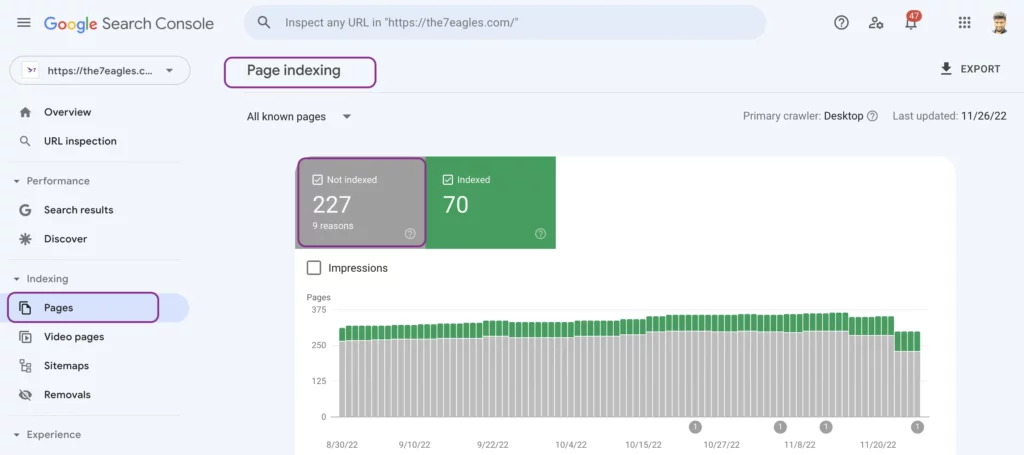
You will get the dashboard which has not indexed and indexed web pages.
Then, select the not indexed tab. It will have all the page indexing issues and the number of URLs affected.
You can choose duplicate, submitted URL not selected as canonical to check all the web pages affected under this coverage issue.
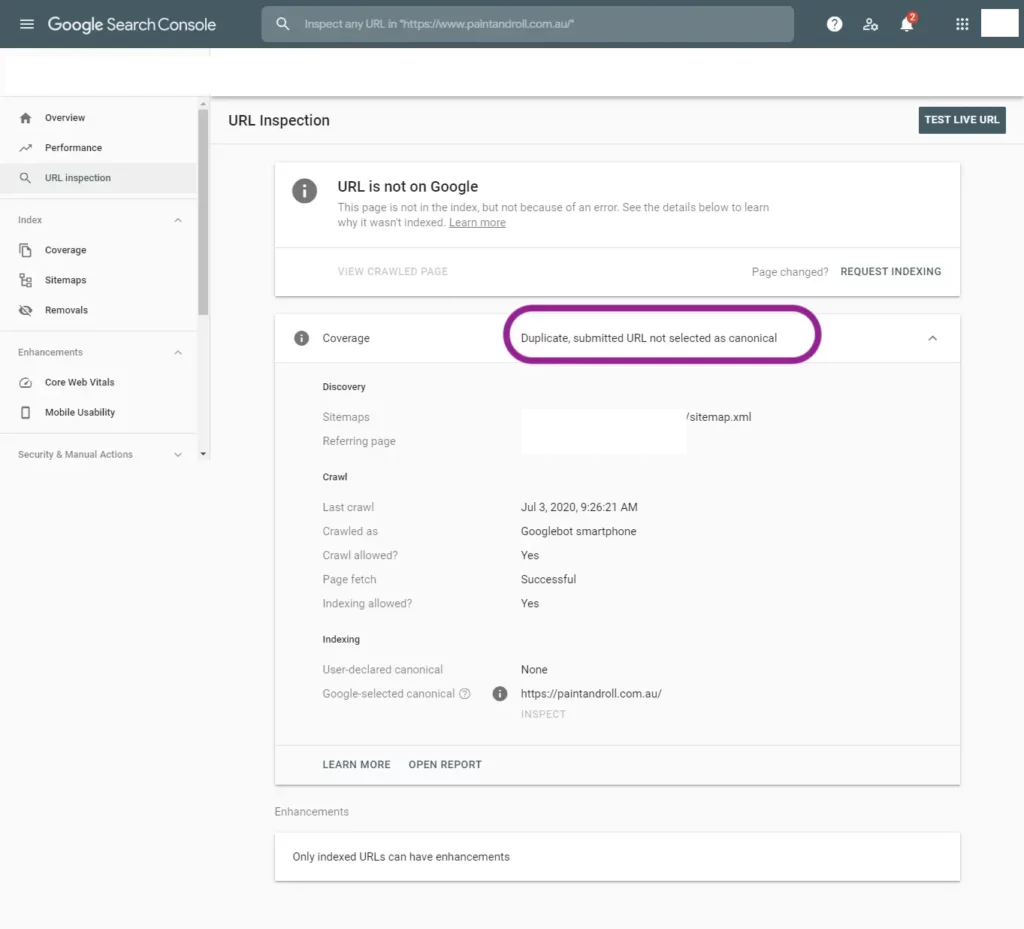
The next way is to do a URL inspection for all the web pages that are not indexed. This will help to find the reason for the web page being excluded from indexing (same as the above image).
How to Fix Duplicate, Submitted URL Not Selected as Canonical?
It is not tedious to fix this coverage issue. You need to analyze whether the affected URL is potential to index.
If the excluded URL is not to be indexed, then use 410 HTTP code or use Removal tool in Google Search Console to remove the URL from Google data base.
Also, check whether the same URL present in XML sitemap and remove them if present.
When the URL excluded is potential to fix, follow these two steps.
1. Validate the Canonical URL of the Web Page:

Here is the above image with HTML codes of a web page, and the highlighted part is the canonical tag of the web page.
<link rel=”canonical” href=” “/>
Scenario 1: If the web page is original, then the canonical URL should be same as the web page URL.
Scenario 2: When the web page is a duplicate version, the canonical URL should be same as original web page URL.
If you find any mismatch in the above two scenarios, then change them immediately.
2. Redirect to the Original Web Page:
If the canonical URL of the web page is correct, but Google has identified the duplicate page URL is canonical, please do the following step to fix the issue:
- Redirect duplicate web page URL to the original Web page.
- Remove all internal links pointing to the duplicate web page.
- Remove the duplicate web page from the XML sitemap.
Once these steps are done, don’t forget to select, validate, and fix in Google Search Console.
Conclusion:
Duplicate, submitted URLs not selected as canonical is a common coverage issue in the Google Search Console.
This issue usually occurs when Google prefers another page as canonical in contrast with the user-selected canonical.
In fact, it doesn’t hurt SEO performance until a potential web page is affected.
If you don’t find ways to fix this issue, you can hire us for holistic technical SEO services.