URL (Uniform Resource Location) is the address for the website on the internet. It identifies a resource’s location and the protocol used to access it. A web address is also known as a URL.
Accessing the resource using a protocol, the relevant server’s address, and where the resource is located in a directory structure. Technically, the “www” is not a part of the protocol. This is a new indicator that websites are using the World Wide Web.
For instance, when you enter the website address https://www.the7eagles.com into a web browser like Google Chrome, the browser contacts the web server hosting the7eagles. The server will react to your request by providing the website’s home page to your browser.
URL vs URI
URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator in its complete form. On the web, a URL is a universal address for documents and protocols used to retrieve resources.
The most common usage of URLs is in relation to web pages (HTTP), but they may also be used for file transfers (FTP), email, database access (JDBC), and many more applications.
- A URL specifies where and how to retrieve a resource, which is a subset of a URI.
- Getting a resource’s location or address is the primary goal.
- The URL is used only to locate web pages.
- The scheme must use a protocol like HTTP, FTP, HTTPS, etc.
- Example of URL: https://google.com
A URI is a string of characters used to specify the location of a physical or logical resource. URI attaches to syntactic standards to guarantee uniformity.
Additionally, it keeps extensibility through a hierarchical naming structure. URI stands for Uniform Resource Identifier in its complete form.
- The URI is a format for identifying a resource using either the URL or URN (Uniform Resource Name).
- A URI is used to locate and differentiate resources based on their names and locations.
- This is used in XSLT (Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations), HTML, XML, and other files.
- Any type of scheme, including a protocol, specification, name, etc., can be used in URIs.
- Example of URI: urn:isbn:0-486-33694-4
URL Structure
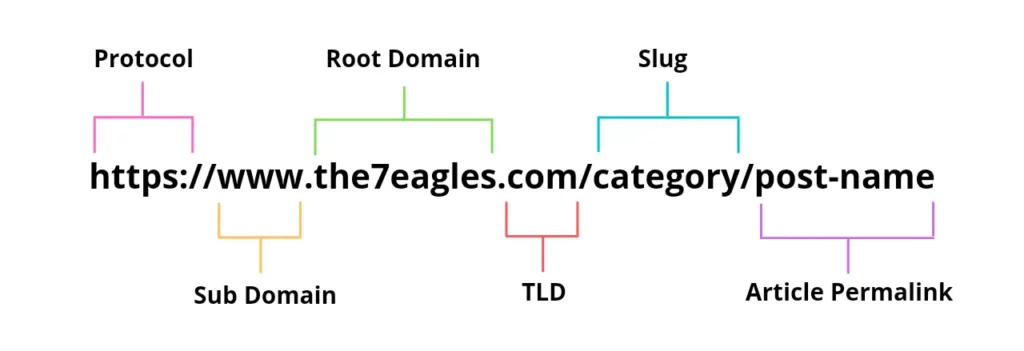
A URL identifies where a web page is located on the internet, and using this address, an internet browser may get the content of that page from a server and display it to a user [source].
The readable text of a URL is made up of various parts. Each component of the URL structure gives particular instructions to a web browser on how to locate and access the content of a webpage.
When creating a URL structure you need to follow these structures
- Pick a format for your URL structure and hold to it; consistency is essential.
- Use keywords to describe the web page’s content in the URL.
- To boost security and trust, use HTTPS instead of HTTP for the URL protocol.
- Keep URLs simple; keep striving not to have more than 80 characters.
- For easier reading, separate words with hyphens (rather than underscores).
- Form in lowercase (no uppercase letters or capitalization).
- Delete certain filler or stop words (a, an, or, but, and).
- Remove punctuation and only use secure alphanumeric characters (including question marks, which are special characters)
- Don’t use special characters for anything other than what they are intended for.
- Do not have more than three levels of folders or paths.
- To keep URLs current and relevant, avoid dates.
- Be less accurate than the page title in the URL.
Parts of a URL
Domain Name: All other pages flow from the main hub of a URL, which is a domain name.
The name of the company or website that appears in the URL is known as the second-level domain (SLD).
Subdomain: A division of a website is a subdomain. Webmasters can structure website parts with various functionalities by creating a subdomain.
Subdomains are frequently created by brands to separate sections for stores, blogs, forums, support portals, and other websites.
Sometimes you can create different pages using subdirectories.
Most SEO experts ask where to use subdomains and subdirectories, here is a blog that has a clear explanation of Subdomain vs. Subdirectory.
Scheme: The scheme is represented by a protocol that the server will use to visit the page.
The HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and HTTPS protocols are the most widely used ones (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure).
Path: The structure of a URL is known as a path that shows the accurate place on the website that the user is trying to access.
It may also include individual page and file names, directories, and folders.
Query Strings and parameters: After the path in the URL, there is a query string that contains information about the result.
Typically, this string appears on dynamic pages like search result pages. There is a question mark (?) at the beginning and then parameters follow.
These are snippets of code that describe how a query has filtered the data.
Fragment: Another URL component that may follow the route is a fragment. The fragment instructs the browser to scroll to a certain portion of the website.
Absolute URL vs Relative URL
Absolute URLs are the kind of URLs that include every component of the URL, such as the protocol, domain name, domain extension, subdomain information, path, query string, URL fragment, and port information.
Compared to relative URLs, absolute URLs are longer and include more data. An absolute URL explains the protocol or the subdomain of the specified website while providing “HTTP,” “HTTPS”, or “WWW” information or without “WWW” information.
Relative URLs only include the portion of the URL that is closely connected. “Protocol-relative URLs” and “root-relative URLs” are the two categories under which relative URLs fall.
URLs that are protocol-relative do not contain information about the HTTP protocol type. It is not necessary to provide the domain name, subdomain name, or extension in root-relative URLs. The current, active URL in the web browser serves as the basis for relative URLs.
There are some differences between absolute URLs and relative URLs for SEO which are listed below.
URL Length: Relative URLs are shorter than absolute URLs.
Informativeness: Compared to relative URLs, absolute URLs offer more details.
Technical SEO: All technical SEO tags require absolute URLs. Only a few of them may be used with relative URLs.
URL Resolution Speed: Relative URLs resolve more quickly than absolute URLs do. Absolute URLs take a longer time to resolve since they are longer.
HTML Size: Each character takes up to 8 KB. Compared to absolute URLs, relative URLs are lighter and shorter for HTML size.
Web Security: It is advisable to use absolute URLs or avoid using protocol-relative URLs because they are bad for user privacy and online security.
URLs with HTTPS and HTTP:
To clarify, the appearance of the TLS or SSL certificate on HTTPS is the primary distinction between HTTP and HTTPS. when Compared to HTTP, HTTPS provides a more secure connection for the transfer of data.
Any information transmitted through HTTP is in “plain text,” which makes it much simpler for hackers to access and manipulate the information by breaking the connection between your website and your preferred browser.
So more than HTTP here HTTPS is typically the greatest option.
The most evident clarification is that it improves in securing user data that contains private data like passwords, credit card numbers, and other sensitive information. However, did you realize that switching to HTTPS may also help your website’s SEO?
www or non-www
Both www and non-www have advantages and disadvantages, but in the end, you must understand the effects of your decision.
If you don’t take care, you can end up with duplicate versions of your website, which would be toxic to its SEO and SERP position. Having a correctly established website URL will help you maintain the flow of visitors.
Before making any changes or reviews. We do not advise switching from www to non-www on already existing websites.
Any decision you make while developing your website (and when search engines begin to index it) is viable.
On well-established websites, you can only make changes if you are sure of your actions and aware of how they may affect how search engines index your website.
Go to your WordPress Admin Dashboard to see if your site is using the WWW or not. Navigate to “General” from “Settings.” then click the categories “WordPress Address” and “Site Address,” and a new page will open. Ensure that both of those are identical (in virtually all situations) and consistent with the domain you bought for the website.
It is important to get advice from the support staff of your hosting provider if you want to make changes.
Importance of URL in SEO
In terms of SEO, URL structure was mostly avoided before. The importance of URLs in Google rankings is now being recognized by SEOs, though.
This main IP address allows users and search engines to understand more about the page’s contents.
As most people are aware, the direct address of a website is essential. Potential clients who are curious about your business will find your website more easily if the homepage URL is memorable.
There have been numerous articles about businesses spending millions of dollars on memorable domain names, adding to the importance of the URL for primary domains.
The significance of all the various URLs that are formed around this primary domain, or the subdomains is on the other hand that is actually rarely discussed in the news.
The characters and structure of these URLs can be the difference between search engines being able to locate all of your site’s pages or none of them ranking at all.
Setting up your URL in the right structure will help you improve your SEO efforts and gain an advantage over your main competitors. You want to make the URL easy and relevant while generating it. By adding unnecessary characters, you run the risk of confusing visitors and search engines.
Keyword in URL Is a Ranking Factor
More significantly, you can notice the use of many keywords in the URL will make reach the page when users search with their keyword knowledge. You may view the search results to see how these keywords are added up in the URL for better reach.
One domain’s URL had the term, whereas the others did not.
These standards were used to develop competing websites on several domains that targeted the same randomly generated keywords
- Among the two domains, one had the keyword in its URL, while the other did not.
- Keywords were mentioned as the first words on both pages.
- There was only one difference in the URL structure.
- Using two different made-up keywords, the test was worked twice.
- It was an unused and new domain.
The results were noticeable. The page with the keyword in the URL was the top-ranked page for both keywords when all pages were indexed and ranked for them.
Best Practices for URL Structure for SEO:
For search engine optimization, making sure your URL structure is appropriate for users in Google search is required. Everyone is aware that a URL must be in lowercase, have hyphens, and undoubtedly include a domain name.
Does the structure of a URL (or URL for those who adds pointless) affect SEO? Yes, it does, and there are really a lot of best practices you should take into account when coming up with a URL for your content.
- Keeping a simple with readable structure.
- To break the words in URL keep hyphens.
- Use lower case in all URLs.
- Do not use words in URL.
- There is no need to match the exact title or headline in URL.
- Ensure that your keywords should appear near the beginning of a URL.
- Do not use more than one domain or subdomain.
- It is better if there are fewer folders (slashes).
- The most important is the verb stem for URLS.
- The quantity of URLs linking to the same or related content should be kept less.
Conclusion:
Though, resources on the internet are identified and navigated by URLs or Uniform Resource Locators. URLs are the entire web addresses of webpages, including the initial portion.
Hope you came to know by this point exactly what a URL is, including its domain name, route, and underlying protocols.
To get the most out of your URLs, keep them simple and to the point. Include the subject of each page in the URL.
When making changes, don’t forget to redirect any outdated URLs, especially those that have already gathered backlinks and were bringing in organic traffic to your website.