Soft 404 is a common Google coverage issue that occurs when a server responds with both a 404 and a 200 HTTP status code while trying to access a web page.
This situation can confuse search engines and users, as it sends mixed signals about the page’s availability and ends up deindexing the potential web page.
If you’re someone who is concerned with fixing soft 404-affected web pages, this article will help you find all the ways to fix the errors.
What is Soft 404? Difference between 404 and Soft 404
A Soft 404 error occurs when a non-existent page — a page that technically should return as a “404 Not Found” message — instead reports as “200 OK” status or vice versa.
A soft 404 coverage issue indicates that the page exists and is functioning correctly, which is incorrect. In terms of technical SEO, Soft 404s are an error, as they lead search engines to believe that a broken page is “OK” to index or vice versa.
As a result, the potential web page that should be indexed returns 404 between the search and search engine— deindexing the web page.
Contrasting Soft 404 and 404 Errors
The difference between a Soft 404 and a 404 lies in the server’s HTTP response to browsers and search engines
404 Error: In simple terms, “Page not found.” When users try to access a URL that doesn’t exist on your server, a 404 error is the correct response. It tells search engines that the page is missing and that they should not index it.
Soft 404 Error: This is not the same as a 404 HTTP response status. The term is instead used by search engines when a non-existent page returns a “200 OK” status, falsely indicating that content is present.
Reasons for Soft 404:
Thin or No Content
Pages that lack substantial content are often flagged as Soft 404s by search engines.
For example,
- Product page without desired description (that doesn’t meet the user’s intent).
- Blog posts that are too short and not helpful to the user, leading users to bounce out of the website.
Such pages are seen as not fulfilling user intent, leading to a Soft 404 status as they essentially serve no purpose to the visitor.
Server Response Error
Technically, the server returns to the client with a 404 HTTP status code (Not found) whenever it encounters a page that has been removed from the website.
However, if the server is misconfigured and returns as 200 (OK) status or vice versa, it becomes an error.
This discrepancy creates confusion for search engines and users, as the response code does not match the actual content (or lack thereof) on the page.
Misconfigured CMS
Content Management Systems (CMS) like WordPress, Joomla, or Drupal are commonly used to build more than 80% of websites across the globe.
If a CMS or its plugins are improperly configured, they might cause pages to respond incorrectly to requests.
For example, a deletion of a post that still returns a 200 status due to a plugin conflict could lead to a Soft 404 error.
Wrong Redirects and Redirect Loops
If a page that has been deleted or moved redirects to a non-relevant page or if the redirect forms a loop (where URLs redirect back to each other), it can result in a Soft 404 error.
Properly managing redirects is crucial to avoiding these issues and ensuring users and search engines are directed to appropriate, existing content.
Dynamic Pages
Websites that generate content dynamically based on user queries or other criteria can sometimes produce pages with no content—for example, a search result page with no results.
If these pages return a 200 status code, they might be flagged as Soft 404s because they don’t provide the expected content to the visitor.
Broken Links
Internal links that point to pages that no longer exist can contribute to Soft 404 errors if those pages incorrectly return a 200 status.
Regular audits of a website’s link structure are necessary to identify and fix broken links, redirecting them to relevant, existing content.
Temporary Content or Placeholder Pages
Websites often use placeholder pages during development or for upcoming sections.
If these pages are accessible to search engines but contain little to no content, they might be seen as Soft 404s.
It’s essential to either block these pages from being indexed until they’re fully developed or ensure they provide sufficient content to be considered valuable.
How to find Soft 404?
Here are the steps you need to follow to find the web pages affected under Soft 404
Step 1 – Log in to Google Search Console
Step 2 – Navigate to the “Indexing” section followed by “Pages”
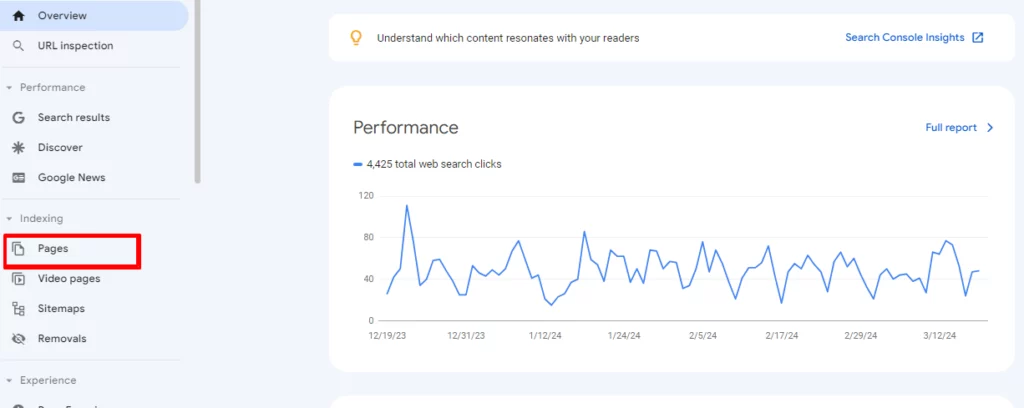
Step 3 – Under the Pages dashboard, you’ll get two options— indexed and not indexed
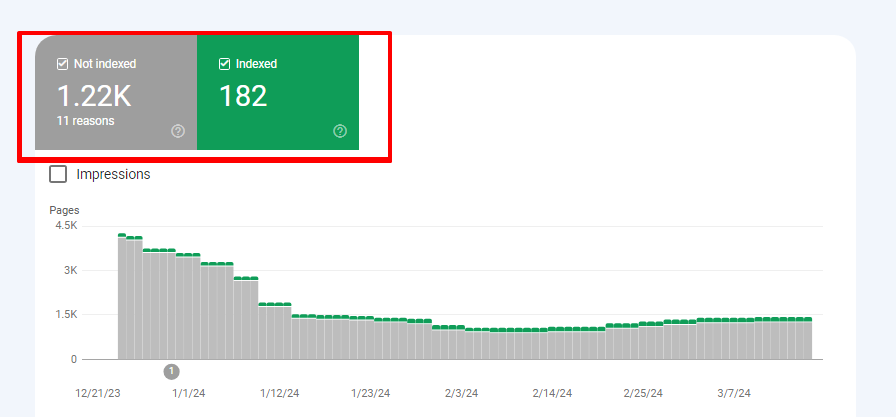
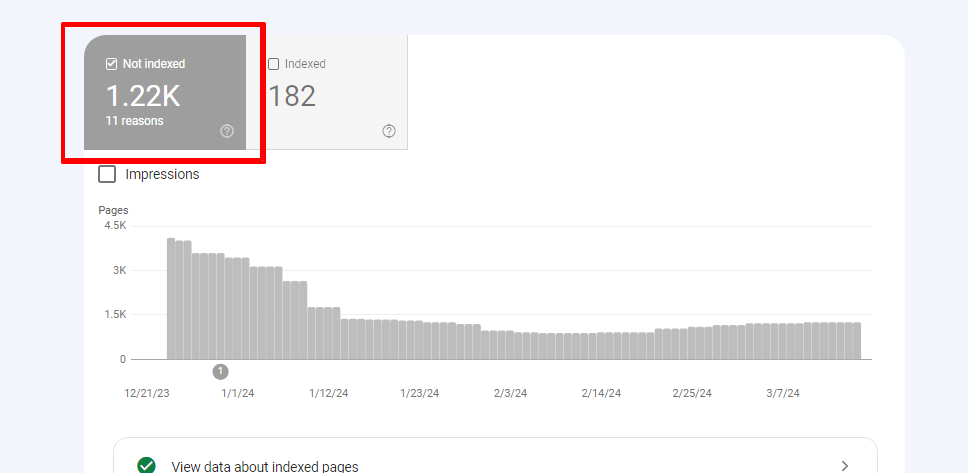
Step 4 – Select only not indexed. You’ll get all the coverage issues of the website— here, you get to know if your website has any soft 404 issues.
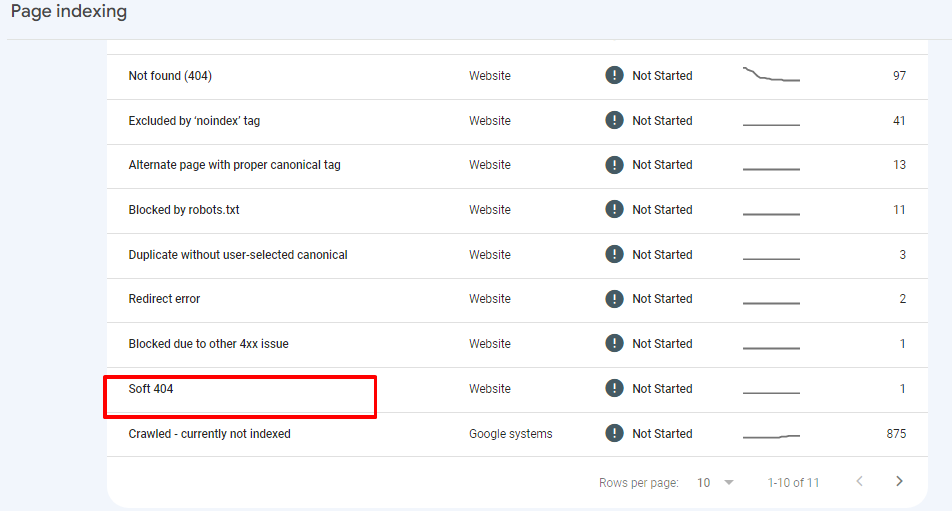
Step 5 – Click soft 404 under coverage issues to get all the web pages affected.
How to fix Soft 404?
Here are 6 proven ways to fix Soft 404 errors and enhance your website’s SEO performance,
Server Errors
Ensuring your web server correctly responds to requests is the first step in fixing soft 404 errors.
Pages that no longer exist should return a 404 (Not Found) or 410 (Gone) HTTP status code.
This clear communication informs search engines that the page should be removed from their indexes.
On the other hand, all potential web pages must return a 200 (OK) status, indicating they should be indexed.
This step requires regular monitoring and potentially technical adjustments to your server’s configuration or .htaccess files to manage response codes effectively.
Content Quality— Make sure it's helpful to the user
When you find thin or no content— fix it by providing helpful content that meets the critical aspects of the user’s query.
Ensure every page on your site, whether a blog post, a product page, or an informational page, offers comprehensive and helpful content to your audience.
Regularly review your site’s content to enrich pages with low content and update outdated information.
Redirections
Improperly managed redirects can lead to Soft 404 errors, especially if redirected pages lead to irrelevant or nonexistent content.
Ensure that any redirects on your site are directed to the indexable web page.
Use 301 redirects to the new location of a moved page, and ensure all internal links point directly to the correct URLs.
Use SEO tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, or Screaming Frog to detect URLs with redirect issues by regularly auditing your website.
CMS Configuration
When configuring your website on the CMS platform, use reputable themes and plugins to avoid configuration issues that might lead to Soft 404 errors.
Always keep themes and plugins updated, as updates often fix bugs, improve performance, and ensure compatibility with search engine guidelines.
Additionally, ensure your CMS settings correctly define what content is indexable and what should remain hidden from search engines to prevent Soft 404 issues.
Use 410 Status
For pages that you have removed, a 410 (Gone) status code is more definitive than a 404.
It tells search engines that the page is permanently removed and not coming back, which can speed up the deindexing process. Use this status for outdated, irrelevant, or otherwise unnecessary content.
False Positives
Sometimes, pages are incorrectly flagged as Soft 404s by search engines. This could be due to temporary content issues, misinterpretations of the page’s purpose, or even technical errors.
If you encounter a false positive, use Google Search Console’s URL Inspection Tool to request a review and reindexing of the page.
This tool can also provide insights into why the page was flagged, helping you make necessary adjustments.
Regular Audits and Monitoring
Preventing Soft 404 errors is done through regular site audits and monitoring using tools like Google Search Console, SEMrush, or Screaming Frog.
These tools can identify not just Soft 404 errors but also other site issues that may affect your SEO performance.
By regularly auditing your site, you can avoid potential problems and maintain a healthy, search-engine-friendly website.
How bad is Soft 404 in SEO?
Misdirecting Search Engines and Users
The user experience is lost when the user clicks on a link and is directed to a page that does not exist.
From a search engine’s perspective, the 200 OK status signal from a 404 (page not found) page implies that the page is valid and accessible, which isn’t the case.
This discrepancy can hurt a website’s credibility in the eyes of search engines, potentially leading to a drop in rankings for not only the affected page but also other pages on the site.
Wasting Crawl Budget
Search engines allocate a certain “crawl budget” for each website, which is the number of pages a search engine bot will crawl on the site within a specific timeframe.
Soft 404 errors can waste this budget, as search engine bots spend time crawling and processing non-existent pages that falsely return a 200 OK status.
This misallocation of resources means less time is spent on valuable, content-rich pages that genuinely deserve attention and indexing.
Causing Indexing Errors and Affecting Visibility
Search engines may index pages that should not be indexed because the crawl budget was wasted on Soft 404 errors.
This indexing can dilute your site’s quality in search results, impacting the visibility of your site’s valid content.
It might lead to significant pages being pushed down in search rankings or not appearing in search results at all, thereby reducing organic traffic and potentially affecting conversions and revenue.
Conclusion:
Soft 404 errors can be a nightmare to SEO efforts, misleading search engines and affecting user experience on a web page’s authenticity.
It’s very easy to identify the web pages affected under soft 404 under the Google search console and start fixing it with immediate effect.
Make sure your content quality, redirection, server, CMS, and plugins are optimized as per the Google’s guidelines to fix or avoid soft 404.
Frequently Asked Questions
Soft 404 Indexing Issue is a common Google coverage issue that occurs when a server responds with a 404 and a 200 HTTP status code while trying to access a web page.
A soft 404 error happens when a webpage that doesn’t exist anymore shows a ‘page not found’ message to visitors but fails to return an HTTP 404 status code.
There are 6 proven steps to fix a soft 404 error
1. Check for Server Errors, 2. Check for thin content, 3. Verify Redirections, 4. Verify CMS Configuration, 5. Use 410 Status for removed pages, 6. Check False Positives.
A Soft 404 returns a 200 (success) status code, misleadingly indicating a successful page load despite the page not existing. This differs from a standard 404 error, usually caused by broken links or dead pages, which correctly indicates that the requested page cannot be found.
Soft 404 affects SEO by misdirecting search engines and users, wasting crawl budget, causing indexing errors, and affecting website visibility.