Ever thought about why certain websites have a .com ending and some other websites have a .org or .net ending?
And that is, The Point of Access to the Digital World, where every click and every tap begins with a simple but effective address called Top Level Domain (TLD).
In the huge network of the internet, where billions of websites compete for audience attention, the Top Level Domain serves as a digital protector, directing users to their destinations and defining the identity of every online entity.
However, What is a Top Level Domain (TLD) exactly? Why is it important in the evolving landscape of Search Engine Optimization?
In this article, From the iconic .com to the niche-specific nTLDs, We will delve into the fundamentals of Internet addressing systems and learn about how TLDs can elevate the online presence to Extraordinary levels.
What is Top Level Domain (TLD)?
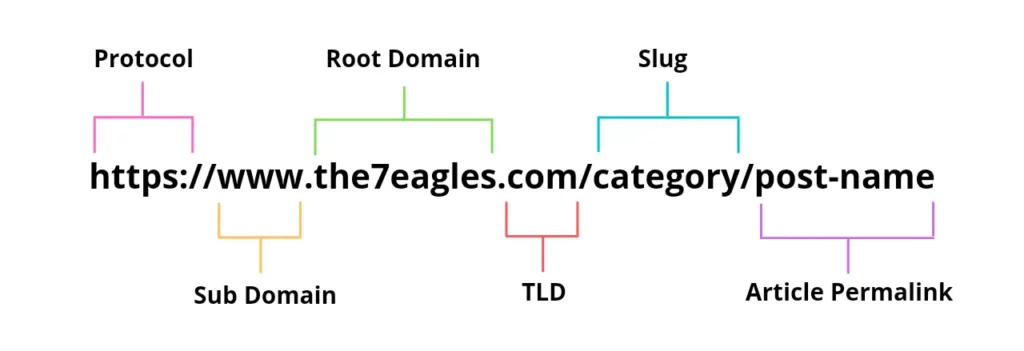
The final part of a Domain Name, to the right of the last dot, is called a Top Level Domain (TLD).
Examples – .com, .edu, .org, .gov, .net.
It corresponds to the highest level in the hierarchical Domain Name System (DNS) of the Internet.
Top Level Domain (TLD) serves as the domain name suffixes, indicating the type and purpose of the website or the organization that owns it.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) and many other domain name registries manage and regulate the Top Level Domain (TLD).
How does Top Level Domain (TLD) Function?
The main responsibility of the Top Level Domain is to classify and organize internet addresses according to their features and intended use.
The following demonstrates the functioning of Top Level Domain (TLD):
- The Process of Identification – TLDs help to identify the type and purpose of a website or the organization that created it.
For Example,
Commercial Websites are identified by .com,
Government Agencies are identified by .gov,
Non-Profit Organizations are identified by .org
- The Process of DNS Routing – TLDs help in navigating internet traffic and it assists the systems to find and connect to the correct servers that are hosting the requested website content.
When a domain name is entered in the web browser, the Domain Name System (DNS) converts the domain name into IP address. So that the device can connect to the corresponding server.
The simplified demonstration of the process is as follows:
For Example, “the7eagles.com” is entered in the web browser,
- The Domain Name System (DNS) checks out the Top Level Domain (TLD) for the .com extension.
- Then the server managing the .com TLD is contacted by the DNS.
- The DNS is then pointed towards the specific servers hosting “the7eagles.com” by the .com TLD servers.
- Finally, the website content is retrieved by the web browser when it establishes a connection with the IP address of 7Eagles’s servers.
- The Administrative Task – Authorized organizations which include both Government and Private entities are in charge of managing and regulating TLDs.
These Organizations monitor the Domain Name registration process within their respective TLDs and ensure the names are unique and resolve disputes when necessary.
- The Hierarchical Structure – Top Level Domains (TLDs) are classified in a hierarchical structure with Generic Top Level Domains (gTLDs) and Country Code Top Level Domains (ccTLDs) constitute the two main groups.
Whereas ccTLDs like .uk for the United Kingdom and .jp for Japan are linked to specific countries or territories and gTLDs like .com and .net are not associated with any specific country.
- The Expansion – The list of TLDs that are currently available has been expanding over time beyond the conventional choices like .com and .org.
The launch of New Generic Top Level Domain like .tech, .blog., .app etc., has allowed for more specific and creative domain naming options reaching out to a wide range of industries and interests.
Impact of Top Level Domain (TLD) on SEO:
Top Level Domains (TLDs) affect SEO, while not Directly or Significantly.
TLDs can impact SEO in the following ways:
- Certain TLDs are owned by reputable organizations or businesses like .com, .org whereas some others are associated with spammy or low-quality websites like .info, .biz etc. When evaluating the trustworthiness of a website, Search Engines may consider the reputation of the TLDs.
- Search Engines can be informed that the website is intended for users in a specific country or region by using country code TLDs like .uk, .ca. This could be advantageous for targeting the local audience, as Search Engines may prioritize local content for relevant queries.
- The choice of TLD can influence how users view the brand. Using a more recent or Niche TLD like .tech for technology-related websites, or .store for an E-Commerce store could help the brand stand out or convey specific attributes.
- Some claim that having keywords in the Domain name with the TLD can have a slight impact on search rankings, though this is debatable.
For Example, Including a targeted keyword in the Domain Name like “keyword.TLD” might offer a slight SEO benefit.
- Backlinks from high-quality websites with reputable TLDs are valuable and positively impact the website’s search rankings.
Types of Top Level Domain (TLD) with Examples:
The different types of Top Level Domains (TLDs) along with examples for each is as follows:
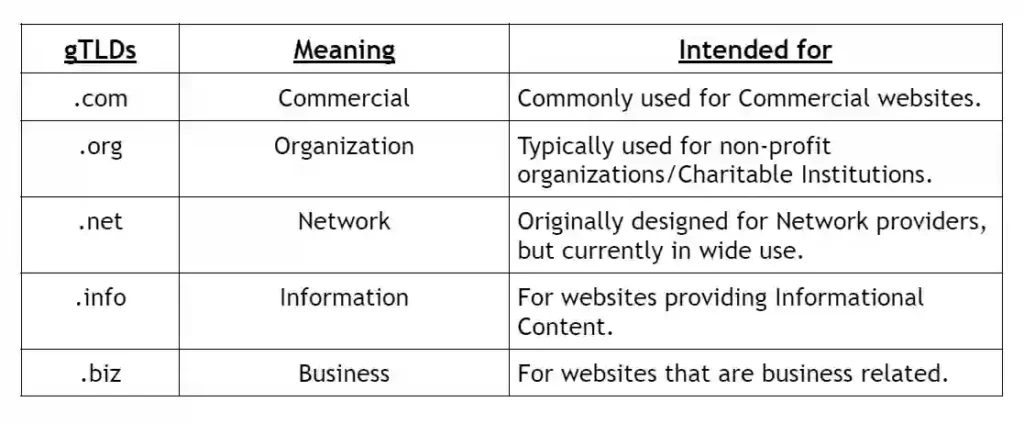
1.Generic Top Level Domain (gTLD)
A Generic Top Level Domain (gTLD) are the most common TLDs and are not associated with any specific country or geographic location.
These TLDs are the most widely used and adaptable. These are often utilized by a broad range of organizations, businesses, and people all over the world.
They provide website URLs, a generic and recognizable extension.
Examples:
2.Country Code Top Level Domain (ccTLD)
A Country Code Top Level Domain (ccTLD) is associated with a specific country or Geographic location.
These are commonly used by businesses, organizations and individuals targeting audiences in specific countries or regions.
These TLDs are assigned to individual countries or territories and are meant to denote a website’s place of origin or Geographical Affiliation.
Examples:
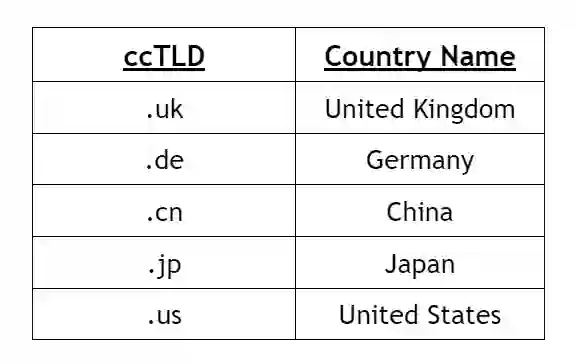
3.Sponsored Top Level Domain (sTLD)
A Sponsored Top Level Domain (sTLD) is managed by private organizations or groups and is used for specific communities or industries.
These TLDs are not open for public registration. sTLDs are managed and operated by sponsoring organizations with specific requirements and restrictions.
Examples:
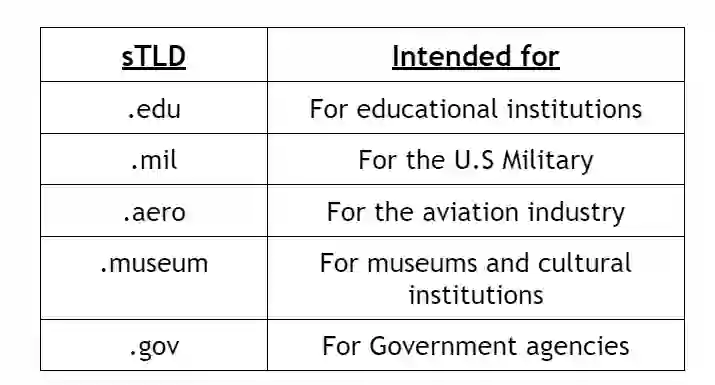
4.Infrastructure Top Level Domain (iTLD)
Infrastructure Top Level Domains (iTLDs) are a specialized category reserved for technical infrastructure purposes.
These TLDs are not commonly used for general website registration but fulfill specific functions associated with the operation and management of the essential infrastructure of the Internet.
Examples:
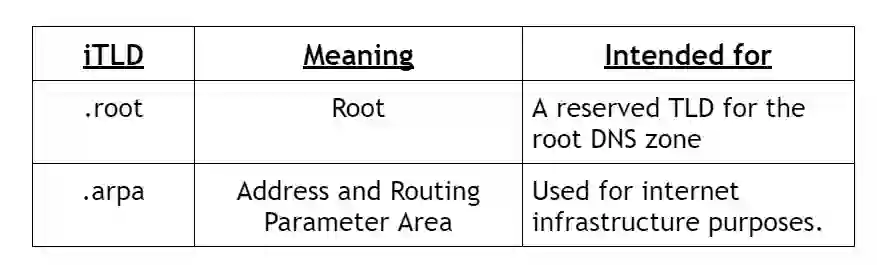
5.New Top Level Domain (nTLD)
New Top Level Domains (nTLDs) are a specific category introduced as a part of an expansion of the Domain Name System (DNS).
These domains offer a wider range of choices beyond traditional TLDs like .com, .org and ccTLDs.
nTLDs offer more specific and descriptive extensions allowing website owners to select domain names that better reflect their business, industry or interests.
Examples:
How to Choose the right Top Level Domain (TLD)?
Selecting the suitable Top Level Domain (TLD) depends upon various factors such as target audience, branding and location-specific focus.
Here are some steps to choose the right TLD:
- Consider the Branding Strategy – The TLD should align with the brand identity.
For a business website, .com TLD is considered the most generic and versatile choice.
It is widely recognized and trusted by the users all over the world.
If the .com extension isn’t available, consider other well-known TLDs like .net or .org.
- Understand the Target Audience – Use a Country Code TLD (ccTLD) like .us, .uk, if the website is intended for a specific country or region.
This can help in demonstrating the users and search engines that the website is related to a specific geographical location.
However, a generic TLD like .com or .net might not be suitable, if the target audience is global.
- Establish the Core Essence of the Website – Certain TLDs are specifically created for particular industries or niches.
For example, .edu for Educational Institutions, .tech for Technology related websites.
Selecting a TLD that aligns with the content of the website can improve branding and make the domain name more memorable.
- Compare Prices and Availability – Verify the availability of the preferred Domain Name in all TLDs before deciding on one.
Consider that certain TLDs might have higher registration fees or renewal costs when compared to others.
When making the decision, consider the long-term expenses and budget into account.
- Consider the SEO Consequences – Although TLDs have a minor effect on SEO, some insist that having keywords in the Domain Name including the TLD can offer a little SEO benefit.
However, prioritize choosing a TLD that best serves the brand and user experience goals ahead of any potential SEO advantage.
- Conserve Brand Identity – To safeguard the brand identity after selecting the primary TLD, consider registering additional TLDs.
This can help prevent competitors or malicious parties from registering the similar domain names with different TLDs and may reduce the possibility of confusion among the audience.
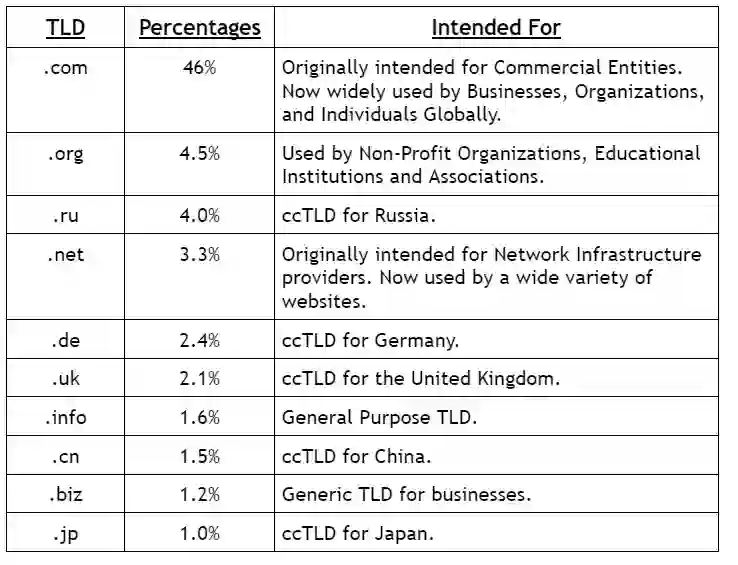
List of most Popular Top Level Domain widely used:
Here is the list of the most popular Top Level Domain widely used with their percentages:
Conclusion:
To Sum up, Top Level Domains (TLDs) serve as the fundamental component for the online presence.
They not only indicate the type of the website, but also have an impact on Search Engine Optimization (SEO) and brand recognition.
With so many options available, from well-known gTLDs like .com to Niche specific choices, choosing the right TLD requires careful consideration of the target audience, the purpose of the website and the budget.
The chosen TLD should be a memorable and strategic component that strengthens the digital identity in the global expanse of the internet.
So, select the TLD wisely and navigate the web that perfectly reflects the brand.
Frequently Asked Questions
The top 5 level domains are as follows,
.com- Commercial
.org- Organization
.net- Network
.int- International
.edu- Education
One of the Country-Code TLDs reserved exclusively for sites located in the Indian Ocean was the io domain.
But now, it is no longer country specific as Google acknowledges it as a Generic Top Level Domain (gTLD) that serves a much wider audience.
A Top Level Domain (TLDs) function is to provide the internet structure and organization by classifying websites into different domains according to parameters such as their intended use, geographical location and affiliation.