When a search engine tries to crawl a page on your website and is unsuccessful, they mark it as a crawl error.
A search engine will attempt to visit each page of your website using a bot during a process known as crawling.
When a search engine bot follows a link to your website, it begins to look for all of your public pages.
The bot indexes all the content for use in Google while crawling the pages, and it also adds all the links to the list of pages it still needs to scan.
Ensuring that the search engine bot can access every page on your website is your major objective as a website owner. A crawling error indicates that Google had trouble examining the pages of your website.
This can hurt the SEO process by creating extensive coverage issues in the indexing and ranking of the resource pages.
What are Crawl Errors?
Crawl errors refer to issues encountered by search engine crawlers when they attempt to access and index web pages on a website.
When search engine crawlers try to attempt the crawling of the pages, if it is unlinked and has any problems, it fails to crawl and those pages comes under crawl errors in GSC.
It’s essential for website owners to regularly monitor and fix crawl errors to ensure that their site is accessible and indexable by search engines.
What Are the Types of Crawl Errors?
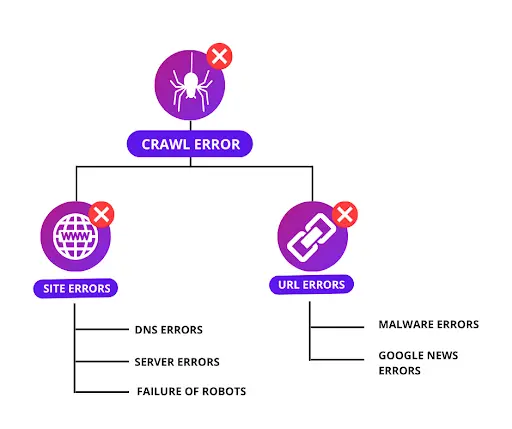
Google separates its crawl problems into two categories: Site errors and UR errors.
Site Error
Site errors are issues that arise on the individual website. All crawl issues preventing the search engine bot from reaching your website are site errors.
This prevents the crawling of your complete site; thus, you don’t want them. So don’t ignore these mistakes. Google recognizes these three are the most frequent ones:
DNS Errors:
- This indicates that a search engine cannot connect to your server.
- For instance, it can be unavailable, making it impossible to access your website.
- Typically, this is a temporary problem.
- Google will still visit and crawl your website in the future.
- If you find warnings about this in your Google Search Console’s crawl errors, it usually means Google tried several times but was unsuccessful.
Server Errors:
- The bot was unable to visit your page if your search console displays server issues. The request could have timed out.
- The search engine attempted to access your site, but the server served an error message since it took so long to load.
- Server problems can also happen when your code contains faults that stop a page from loading.
- It might also imply that there are so many people visiting your website that the server is just overwhelmed with requests.
- Many of these problems, including the 500 and 503 status codes, are returned as 5xx status codes.
Failure of Robots:
- In order to determine whether there are any portions of your website, you’d prefer not to have indexed.
- Googlebot tries to browse your robots.txt file as well before crawling.
- If the bot is unable to access the robots.txt file, Google will delay the crawl until it can.
- Make sure it’s accessible at all times.
URL Errors:
- When a search engine bot tries to crawl a certain page of your website, URL problems happen.
- Although you also don’t want these, they are simpler to monitor and correct because each problem only pertains to a particular URL.
- When talking about URL errors, we frequently start by talking about crawl errors like soft 404 or Not Found messages.
- We can use tools like Google Search Console or Bing webmaster tools to regularly check for and correct this kind of mistake.
- Serve a 410 page if the page or its subject is truly gone from your website and will never come back. Please use a 301 redirect if another page contains identical content.
- Naturally, you should also check that your sitemap and internal links are current.
- By the way, we discovered that many of these URL issues are brought on by internal links. So a lot of these mistakes are your own.
- Adjust or remove any inbound links to any pages that you ever decide to remove from your website. These links are no longer useful.
- A bot will find and follow the connection if it stays the same only to come to a dead-end, i.e., 404 Not found error through your website. You should occasionally perform some maintenance on your internal links.
- The URL error with the phrase “submitted URL” in the title is another typical URL error. These issues start to show up as soon as Google notices irregular behavior.
- On the one hand, you requested that Google index the URL, informing it that you want this page to be indexed.
- However, something else is requesting that Google not index this page. Your robots.txt file may be the cause if it is blocking access to your page or that a meta tag or HTTP header places a “noindex” designation on the website.
- Google won’t index your URL if the inconsistent message isn’t fixed. Some URL mistakes only affect specific websites.
We’d prefer to list these separately for that reason:
URL errors were particular to mobile:
- This is a reference to crawling issues that only affect a certain page on a modern smartphone.
- These are unlikely to appear on a responsive website.
- Maybe just for that particular piece of Flash material, you previously intended to replace.
- You can see additional issues if you keep a separate mobile subdomain similar to incorrect redirection from your desktop website to that mobile website.
- You may have even added a line to your robots.txt to prevent portions of that mobile site.
Malware Errors:
- Malware errors in your webmaster tools indicate that Google or Bing have discovered harmful software at that URL.
- This could imply the discovery of software that is employed. For example, to obtain guarded information, or to undermine their operation generally, you must look into that page and get rid of the spyware.
Google News Errors:
- Some particular Google News inaccuracies exist.
- If your website is listed in Google News, you may encounter one of the many crawl issues listed in Google’s guidance.
- They range from problems informing you that your page doesn’t appear to include a news story at all to the absence of a headline.
- If this pertains to your site, be sure to confirm it for yourself.
How to Find Crawl Errors?
You can find crawl errors by using various tools. Here are some common methods to find crawl errors:
1. Google Search Console
- Sign in to your Google Search Console account.
- Select your website property.
- Under settings you can see the crawl stats
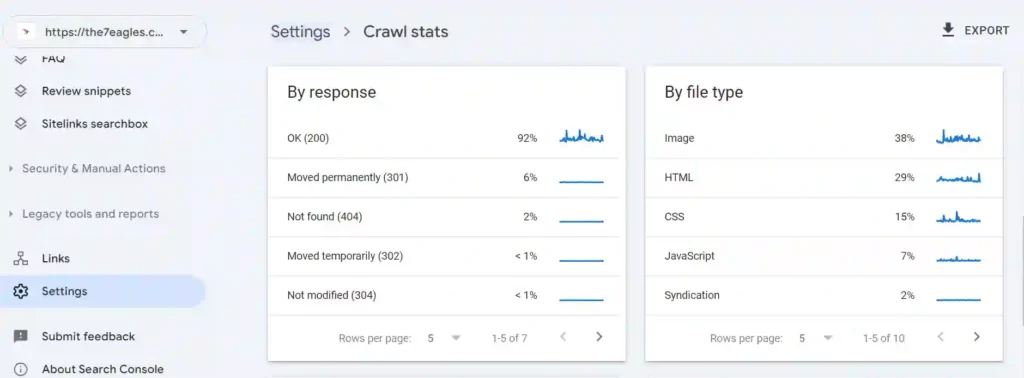
Here you can see any crawl errors detected by Google, including URLs that couldn’t be indexed.
2. Website Audit
Site auditing tools like Semrush, Ahref, and Screaming Frog can be used to find the crawl errors on your website. Some of the SEO site audit tools are free and some are paid.
Conclusion
Crawl errors seriously affect the performance of the website, so it is important to fix those errors immediately so that you have all your pages in the search engine results page
Need help in fixing technical errors including crawl errors, check out our technical SEO services and connect with us.
Frequently Asked Questions
Crawlability issues stop search engines from reading websites. These issues prevent sites from appearing in search results properly.
Crawl errors occur for various reasons: broken links, server issues, redirects, and access restrictions. Mistyped URLs, deleted pages, server overload, and misconfigured settings also contribute. visibility in search results.
Crawling for SEO involves search engine bots systematically browsing and analyzing web pages to index their content. It’s a crucial step in SEO as it helps search engines understand a site’s structure, content, and relevance.
The crawl rate in SEO refers to the rate at which search engine bots, such as Googlebot, visit and crawl a website’s pages. It’s determined by various factors, including the site’s authority, server speed, and crawl demand.
You can check for crawl problems using Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools. Third-party SEO tools like SEMrush, Moz, and Ahrefs also offer crawl analysis.